What to Know Before Buying Insulated Wire
From the most basic cable assemblies to intricate custom cable assemblies, insulated wire is found in some form. It’s wide range of uses makes it popular for many kinds of projects, but before you get started, it’s important to do some homework on the wire you plan to buy.
How will it hold up under pressure?
This can encompass a range of issues, but when choosing wiring for a cable assembly, you need to consider what that assembly will go through, and look into the specs of your wiring before you buy. Specific things you should look for include the cable’s optimum temperature range for operation, it’s resistance to water and humidity if it will be in a damp place, and whether it has the flexibility to fit into the type of space you’re working with.

What is its usage rating?
Along with checking how the insulated wire and cable will work in less than ideal conditions, be sure to check how those conditions will affect its usage rating. Every cable is assigned a rating which states the maximum current that can be passed through that wire, along with a maximum temperature for the surface of the conductor. Wires that are commonly used in cable assemblies installed in extreme places, have several ratings, one for its use under ideal circumstances, and one for use in wet places, or places with extreme temperatures. By checking this beforehand you can avoid having to do costly repairs or a full replacement down the road.
What method was used for marking the cable?
This may not seem very important, but the way the cable was marked can make a big difference in its quality. Cables marked by hot stamping are more likely to have damaged insulation or exposed wired due to the pressure on the insulation during the marking. Problems caused by poorly done cable marking are particularly important to look out for when doing large scale cable assembly, when one bad wire can undo a whole lot of work.
Knowing the capacity of your wire before you install it, choosing the right kind of wire for the job, and being able to avoid damage-prone wires makes a huge difference in both basic and custom cable assemblies. If you are unsure of what kind of insulated wire to buy, be sure to consult a professional to avoid expensive repairs or worse, replacements.
*Remember each situation is unique and this is generic information, always consult a professional before making any decision.
Why Outsource?
Outsourcing has become a hot topic in recent years. You may already be aware that the concept of outsourcing is far from a new idea. As far back as 1776, economist and philosopher Adam Smith addressed the topic is his seminal volume An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations. He has been quoted as saying “If a foreign country can supply us with a commodity cheaper than we ourselves can make it, it is better to buy it of them.”
 In recent years many companies have viewed outsourcing as a business fad or trend to partake in without understanding the true benefits and potential risks that outsourcing can provide their organization. Any manager or executive knows that the effective utilization of organizational resources directly impacts a business’ bottom line. Process improvement, specialization, and task proficiency may not be optimized within your business. If this is the case, you may be able to deliver a better product at a lower cost by outsourcing certain aspects of your business to a firm that can provide these benefits. This enables you to offer your end customer a better product of service and keep your organization focused on what they do best.
In recent years many companies have viewed outsourcing as a business fad or trend to partake in without understanding the true benefits and potential risks that outsourcing can provide their organization. Any manager or executive knows that the effective utilization of organizational resources directly impacts a business’ bottom line. Process improvement, specialization, and task proficiency may not be optimized within your business. If this is the case, you may be able to deliver a better product at a lower cost by outsourcing certain aspects of your business to a firm that can provide these benefits. This enables you to offer your end customer a better product of service and keep your organization focused on what they do best.
For example, if you are located in California and you sell a product primarily in US but do not have the ability to design, manufacture and source materials of the highest quality locally should you settle for what you can do locally and offer your customer a lower quality, higher priced product? Or should you find a company that specializes in the areas you are deficient in, and outsource those functions? That is a business decision you will have to make, however, industry leaders are realizing that everyone wins when companies focus on their core competencies and outsource other functions to a firm who specializes in that area.
Outsourcing non-critical processes to third party firms with more expertise guarantees that your company’s resources are available for critical activities where you do have an expertise. Remember, your partner can supplement your operations and provide additional capacity as needed without the overhead costs your firm would incur if handled on-site. Organizations that outsource often discover that costly infrastructure expenditures are drastically reduced as some functions are outsourced to external locations.
Many successful firms outsource work in order to have their processes delivered by companies with operational expertise in that particular outsourced process. Outsourcing can provide your firm access to exceptional capabilities and infrastructure in terms of the outsourced function. Also, depending on where your firm is located, outsourcing may offer additional incentives both economic and cultural.
Take for example an American firm outsourcing to Canada. Due to the exchange rate, for every dollar an American firm spends in Canada, that firm receives over $1.10 worth of goods and services. Additionally, Canada and the United States share similar cultures and regulatory climates as well as they shares the same aesthetic, quality and core competency values as their American counterparts. The fact that transportation costs and lead times are the same as having a supplier across the other end of state further reflect on the bottom line, and equally quickly. Canada’s cost of labor is lower than the U.S. and Canada has distinctive strategic advantages that firms located elsewhere cannot offer.
Once you assess your business’ strategic needs and begin to select outsourcing vendors, make sure that the firms you consider can accommodate your needs and unique requirements. Outsource correctly and your company will have a competitive advantage over others in your industry.
STP vs UTP Cables: Application Comparison
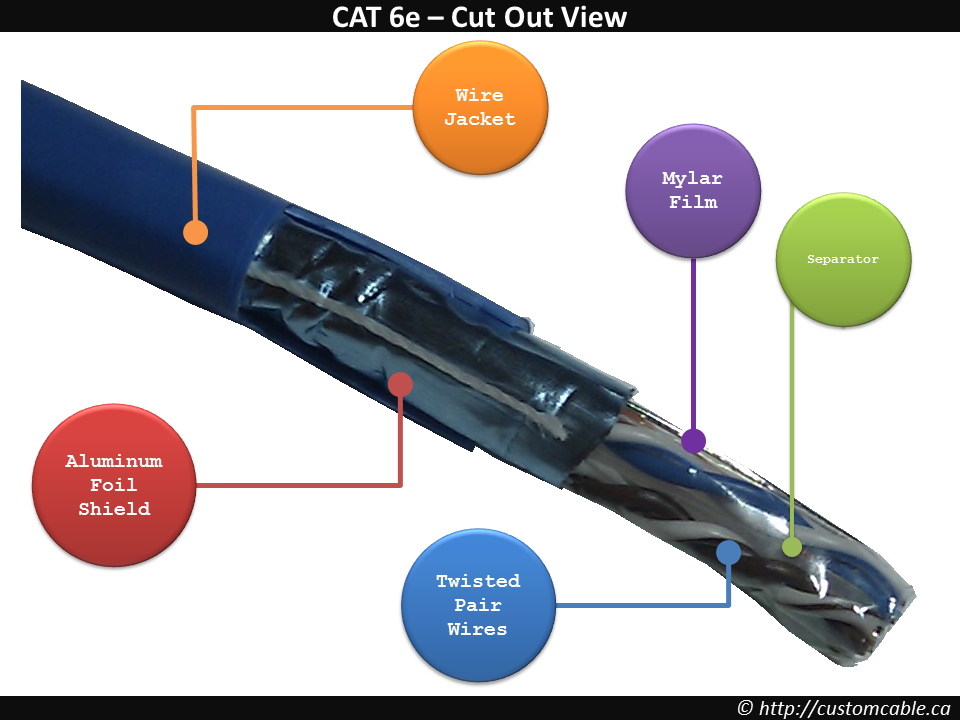
Differentiated physically by little more than a conducting shield, shielded twisted pair cables and unshielded twisted pair cables nonetheless have different advantages, disadvantages, and best applications.
Both shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP) have interference canceling capacities, however the way that each one is designed to cancel the interference is different. Interference caused by power lines, radar systems or other high power electromagnetic signals, called noise, can cause an imbalance in the current flowing through the shield or conductors of the cables which interferes with the signal. STP cables have a conducting shield made of metallic foil encasing the twisted wire pairs, which blocks out electromagnetic interference, allowing it to carry data at a faster rate of speed.

However, they have several disadvantages. STP cables work by attracting interference to the shield, then running it off into a grounded cable. If the cable is improperly grounded, then its noise-canceling capabilities are severely compromised. Additionally, STP cables are bigger than UTP cables, and are more expensive. Finally, they are more fragile than UTP cables, as the shield must be kept intact in order for them to work properly. The best use for STP cables are in industrial settings with high amounts of electromagnetic interference, such as a factory with large electronic equipment, where they can be properly installed and maintained.

UTP cables are the most commonly used cables for ethernet connections, and have a number of advantages. They rely on the cancellation affect caused by the twisting of the wire pairs to handle noise, which is more than enough for most domestic uses. They are also smaller than STP cables, which makes them easier to install, particularly in bulk or in narrow spaces. They are easier to install than STPs, and do not require the presence of a grounding cable. UTP cables are also cheaper than STP cables, and do not require as much maintenance, since they do not rely on an outer shield, and can transmit data as fast as STP cables. However, they are more prone to noise than properly installed and maintained STP cables. They are best used for domestic and office ethernet connections, and in any area where there is not a high degree of electromagnetic interference.
While both STP and UTP cables have their pros and cons, when installed and maintained properly in a situation appropriate to their uses, both work perfectly fine.
Lean versus Agile Production
It was in 1989, that for the first time the world was introduced to the term ‘lean production’ as it was coined in by MIT. On the other hand, Agile Manufacturing can trace its origins in a research study by Lehigh University in the early 90s.
Before discussing lean and agile, it’s important to place lean manufacturing in context with the traditional mass production principles. Lean manufacturing does away with many of the manufacturing principles, and guidelines of mass production. A brief comparison is tabled below:
Mass production |
Lean Production |
| Inventory Buffers | Minimum Inventory |
| Just in Case deliveries | Just in time deliveries |
| Acceptable Quality Level | Perfect first time Quality |
| Taylorism | Worker Teams and Worker Involvement |
| Maximum efficiency | Flexible production systems |
| If ain’t broke, don’t fix it | Continuous improvement |
| Minimum waste |
Adapted from Mikell P. Groover’s Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2nd Edition
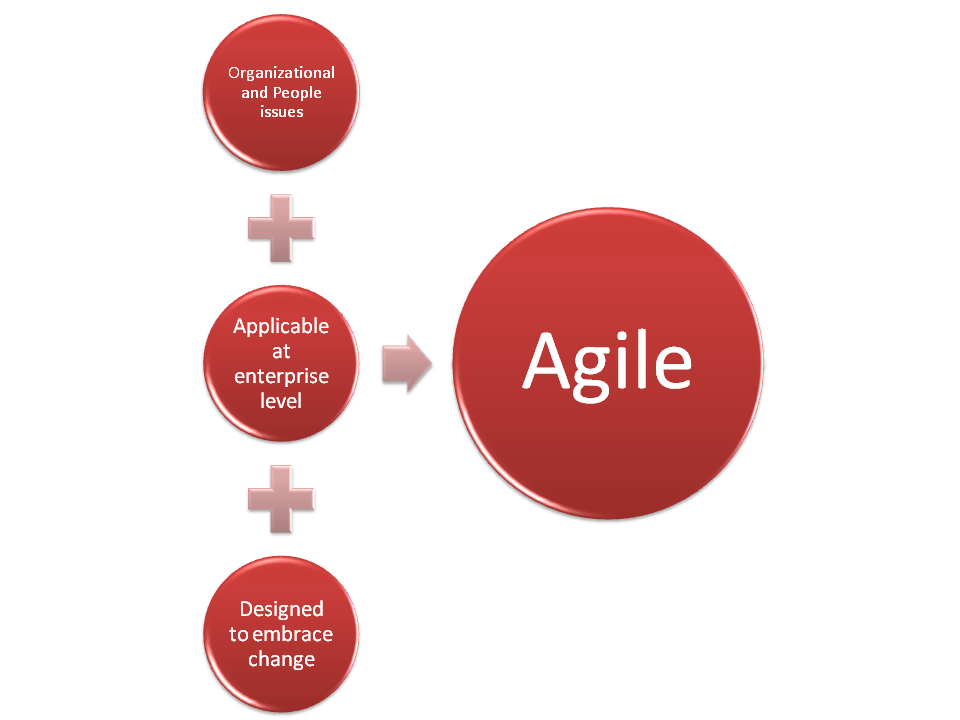
Although, tabled nearly at the same time as Lean Manufacturing, it is indeed Agile manufacturing which is far more relevant to the North American manufacturers at the enterprise level, than the former. Reason is simple enough; today many North American manufacturers are primarily focused on producing customized solutions as per client specs and in small to medium sized batches. Today quantities as little as 500 to 1000 pieces of practically any product can be outsourced to offshore vendors with considerable cost advantage.
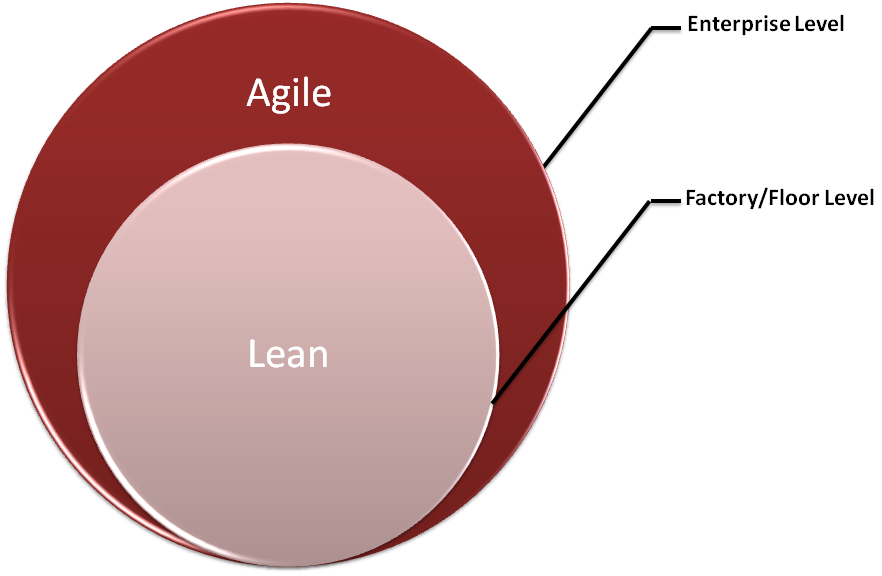
It is important to remember that lean allows for waste free, efficient system that adds to the bottom line and in turn give competitive pricing advantage. However, most customers today come to local manufacturing facilities for their ability to quickly adapt to changes, better technical support, shorter time to market and most importantly, short production runs. Consequently, absolute focus on lean production may not be suitable for most local manufacturers and application of agile manufacturing principles on the enterprise level is important to maintain competitive against local and overseas competition.
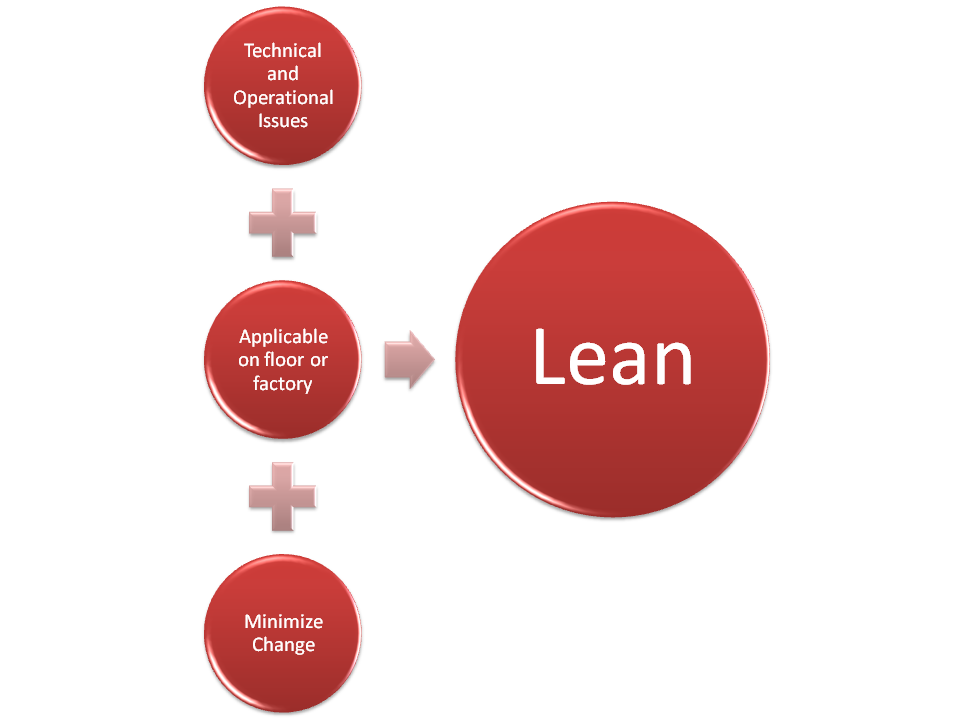
Lean and agile principles complement each other, however, the scale at which they are applied are different. Lean principles are best applied at the factory or floor level where efficiency takes precedence of all except safety. On the other hand, agile principles are most suitable at the enterprise level where ability to adjust to changing internal and external factors is off utmost importance. The emphasis in lean is more on the technical and operational issues, while agile addresses the people and organizational issues.
However, where there is a significant difference is how change management is performed under each system. Lean tries to minimize change, whether internal or external in order to minimize waste and increase efficiency. Whereas, agile embraces change. The idea is to thrive at the ever changing environment and business landscape.
In fact, agile manufacturing should be seen as the natural extension and evolution of the lean principles.
Four Principles of Lean Production and Agile Manufacturing
Lean Production |
Agile Production |
| Minimize Change | Enrich the Customer |
| Perfect first-time quality | Cooperate to enhance competitiveness |
| Flexible production lines | Organize to master change |
| Continuous improvement | Leverage the impact of people and information |
Adapted from Mikell P. Groover’s Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2nd Edition
Comparison of Lean Production and Agile Manufacturing Attributes
Lean Production |
Agile Production |
| Enhancement of Mass Production | Break with mass production; emphasis on mass customization. |
| Flexible production for product variety | Greater flexibility for customized products |
| Focus on factory operations | Scope is enterprise wide |
| Emphasis on supplier management | Formation Virtual enterprises |
| Emphasis on efficient use of resources | Emphasis on thriving in environment marked by continuous unpredictable change |
| Relies on smooth production schedule | Acknowledgement and attempts to be responsive to change. |
Adapted from Mikell P. Groover’s Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2nd Edition
Stranded vs Solid Wire
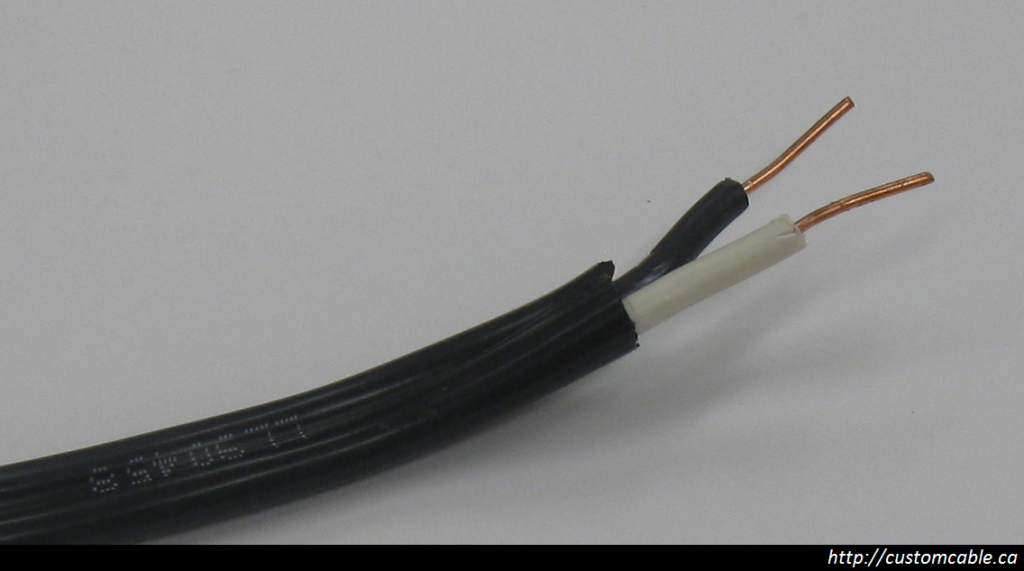
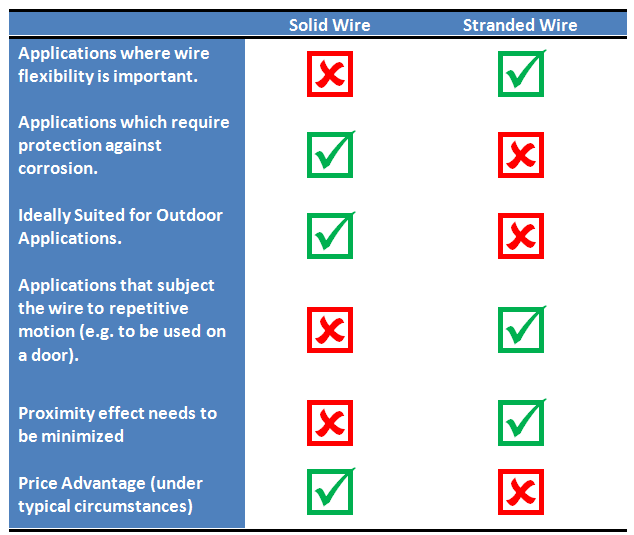
In choosing the right type of wire for a project, there are a number of important considerations. Based on the amperage load and application, the electrician needs to determine the appropriate gauge of wire to use, as well as the type of metal wire to use. Beyond choosing between aluminum or copper, the wiring expert will understand the difference between stranded and solid wire and will choose the appropriate wire core to use for their chosen project. While solid wire consists of a single metal core, a stranded wire is composed of numerous thinner wires twisted together into a cohesive bunch. Both types of wire are appropriate for commercial and residential installation, however each has particular advantages and disadvantages that lead to the choice of one over another for each particular application.
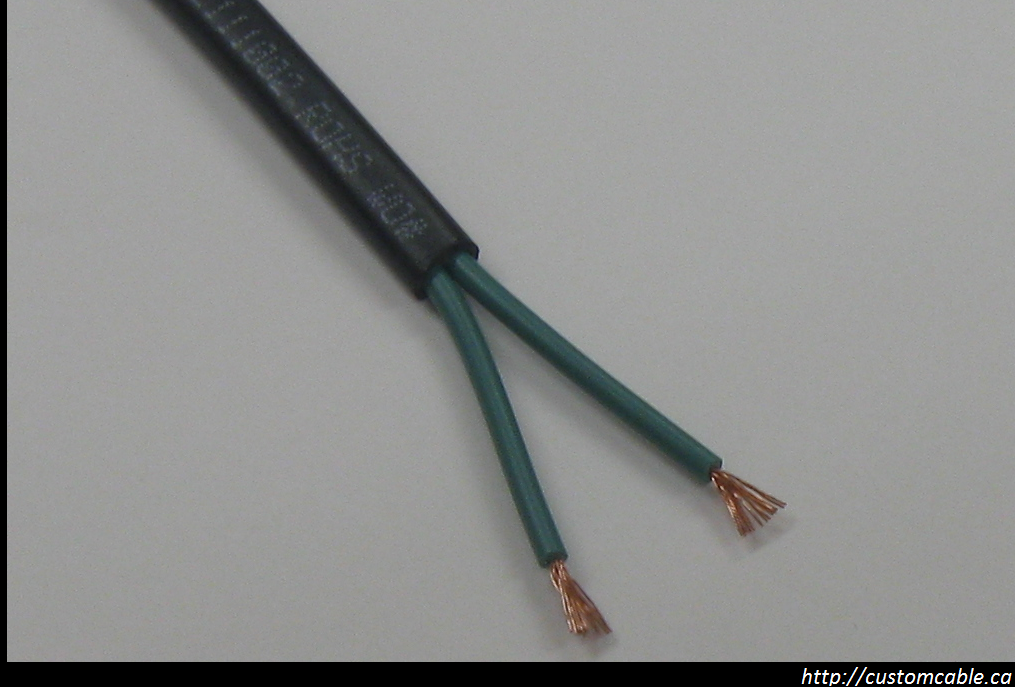
While both types of wire will transmit electricity effectively, each is better suited to specific applications in both residential and commercial uses. Solid wire is the wire of choice for outdoor or rugged-duty applications which may expose the wire to corrosive elements, adverse weather condition or frequent movement. Stranded wire, conversely, serves a better purpose in intricate usages, such as electronic devices and circuit boards, where the wire will be protected but may undergo bending or twisting in order to connect electronic components.
The advantage of solid wire is one of cost, simplicity and durability. Because it is merely a single, thick strand of wire, the wire is very resistant to damage and extremely simple to make. However, for applications which require a great deal of movement — such as robotics or vehicular applications — or will require the wire to be bent into complex shapes — such as electronics and circuit boards — solid wire is undesirable because it lacks the strength and malleability to endure reshaping and motion. On the other hand, stranded wire is well-suited to applications which will demand flexibility and reshaping. For preventing electronic interference, however, stranded wire holds a disadvantage because the air channels between strands magnify the skin effect caused by magnetic fields on the surface of the wire.
In choosing based on cost, initial cost needs to be weighed against long-term durability. While a solid wire initially costs significantly less to purchase than stranded wire, a stranded wire will last longer in environments where motion or frequent alterations to the wiring may occur. All of these factors need to be taken into account before making a decision about the type of wire to choose for an application.
*Remember each situation is unique and this is generic information, always consult a professional before making any decision.
Five Connectivity technologies for 2010
A number of new technologies were introduced in 2009 for end user product connectivity, we pick our favorites for ones that are sure to generate some serious consumer interest in 2010.
1 – HDMI 1.4
Great breakthroughs have been made this year concerning HDMI technology for 2010.Cunsumers should be excited about all the new features regarding Internet connectivity, higher color definition, better sound and more options when it comes to devices the new HDMI 1.4 standard can support. Previous HDMI standards could only support 1080p video resolutions and a limited amount of audio formats. Added connectivity support includes:
- Ethernet channel support: This will enable users to utilize 100Mb/Second transfer rate without the need for additional network cabling.
- Audio upstream channel: This will allow a single cable connection for users who have devices that require post audio processing, eliminating the need for additional cables.
- 3D over HDMI: Enables typical 3d formats to be standardized while adding duel 1080p streams between capable devices.
- 4K x 2K Resolution Support: Probably one of the most exiting features of the new HDMI 1.4, this technology will allow for high definition screen resolutions up to 4 times that of previous HDMI standards. Up to 4096×2160 at 24Hz and 3840×2160 at 24Hz/25Hz/30Hz resolutions will be possible. Earlier HDMI capabilities only have a maximum resolution of 1920×1080.
- Expanded Support For Color Spaces: This addition will add crisper images and more defined color when connected to a capable digital camera.
- Micro HDMI Connector: Almost half the size of existing mini HDMI connectors, this 19 pin cable will enable connections for capable portable devices with high definition resolutions up to 1080p.
- Automotive Connection System: With the vehicle environment becoming more media oriented, this technology will bring high definition capabilities to cars and trucks. Many strides have been made in this area in terms of durability and reliability, as vehicles can experience harsher climates, increased vibration and noise interference.
2 – Display Port
Display port is one of the latest video, audio and data connection standards offered by VESA. The technology is open source and many other connectivity formats are supported, such as Ethernet and USB. Display Port is designed to replace older technologies such as DVI, LVDS and VGA connection types commonly associated with most of the personal computers used today. This new technology will enable consumers to do away with many older connection technologies, making it possible to use one Display Port connection cable to operate a multitude of devices. Some of the key features of Display Port are:
- Connecting external devices such as multiple monitors, webcams, USB peripherals, networking devices and audio components, all in one simple cable.
- Full HD 3D support: Over 240 frames per second are possible with Display Port 1.2 and up to 4 monitors at full 1080p. For a single monitor, this technology can support resolutions up to 3840 x 2400 at 60Hz.
- Support for High Definition audio formats such as Dolby MAT, DTS HD, Blu-Ray, and the DRA standard.
3 – Category 7 Networking Cables
Until now, network cabling technology has undergone very few changes. As with any copper wiring, electrical interference can cause problems with data transmissions over network cabling just the same. Users of these newer networking standards will allow the user to surf the Internet faster and more reliably as well as transfer files among connected computer systems at blazing speeds without any hiccups.
- Cat 7: This standard will simply allow for better resistance against such natural and manmade electrical interference to allow for a more stable and reliable connection between networked devices. An increase in data transfer rate is also possible, up to 10 Gigabits per second over a 100 meter span. Previous Cat 6a can achieve this speed; however, with the new standard this high speed connection will be more consistent.
- Cat 7a: Similar to Cat 7, the improvements planned for this standard have not been fully implemented. The noticeable differences will include an increase from 600 MHz to 1000 MHz in terms of frequencies that can be utilized for data transmission.
4 – USB 3.0
USB 2.0, while serving users well for over a decade, has shown its age and as the demand for higher data transfer rates have increased, so has a the need for improvement. An increase of speed at almost tenfold is expected with USB 3.0. The new standard should be available on many new computers and other compatible devices sometime in 2010. Not only will the consumer be able to transfer High definition videos and pictures up to 10 times faster than USB 2.0, users will see a dramatic decrease in power consumption among smaller USB 3.0 enabled devices.
- USB 3.0 will allow for simultaneous bidirectional data transfers. With the older USB 2.0 specification, it was only possible to read or write information one direction at a time.
- Major data protocol changes have been made with USB 3.0. Earlier USB host controllers would constantly check a connected device for an incoming signal. This newer standard changes that by allowing the connected device to instead send a signal to the host device when it is ready to communicate, thereby freeing up resources and saving energy in the process.
- USB 3.0 is backwards compatible with preceding technologies, giving the new standard more flexibility.
5 – Wireless HDMI
Wireless technology has become the new data exchange frontier for the new millennium. HDMI is the gold standard when it comes to transmitting and receiving high definition video and audio. Wireless HDMI will allow consumers to transmit 1080p video and HD audio formats without the need for obtrusive cables. Many television and other various multimedia product manufacturers have implemented this new technology with their latest offerings. Although this new wireless standard is fairly new and expensive, it is believed that wireless HDMI will become common place in the near future.
The current downside to wireless HDMI is the limited range of the technology. Range limits have put into place because of the extraordinary frequency range used to transfer the amount of data required for the transmission of high definition data. Stronger signals produced by wireless HDMI devices could possibly interfere with other wireless components in or around the home. Current consumers who have jumped early on the bandwagon have complained about the component noise produced from cooling fans used in certain wireless HDMI devices that are available on the market today.
We hope you enjoyed the read, and wish you a very happy new year.
Electromagnetic Fields and Public Safety
The controversy is ongoing as to whether electric or magnetic fields have a harmful effect on people living near them. A look at the most recent studies, covering electromagnetic wave emissions and their effect on living cells seem to be inconclusive at worst and show no effect at best.

A recent study by the National Academy of Sciences/National Research Council Report: Possible Health Effects Of Exposure To Residential Electric And Magnetic Fields, in regard to people living near high-power lines found no higher risk for cancer or other health effects than in a normal population living away from such lines. A similar university study found that pastures and fields where a power line crosses had no measurable impact on the animals living in the area.
All electronic equipment produces some form of electrical or magnetic field. Even wire harnesses and custom cable installations put out an electrical field. Everyone is exposed at some point during the day to one of these fields which are present wherever we run power cables and use electronic devices. They are so ubiquitous in our environment we generally never notice them around us.
Starting in the 70’s a vocal group of people started complaining about high power transmission lines being built near their homes. People used anecdotal evidence to try and blame the electric field generated by the power lines for increased risk of cancer, and other medical problems. The power companies naturally were concerned, and sponsored studies and tests to try and prove whether the fields were safe or not.
One of the main illnesses that electromagnetic waves have been accused of causing is childhood leukemia. However there have been two studies, one by the National Academy of Sciences, and the other by the National Cancer Institute which found no correlation between exposure to high electromagnetic fields and the disease. The World Health Organization has issued a fact sheet that states there is no substantiated evidence to link the disease with ELF and EMF radiation.
These studies, done by leading research institutes and universities have so far shown no correlation between electric fields and human illness. Most of the cases that were used as proof were found to fall within the normal statistical variation for the general population for getting the illness.
This is not to say that all electromagnetic radiation is safe. At higher wavelengths these harmless waves can become harmful radiation such as x-rays and gamma waves. It is however, impossible for power lines to generate this type of radiation.
There are still those who worry, and who use anecdotal evidence to make a straw man out of power lines. The science however, does not support them. After the NCI studies were done the US government shut down a US department of Energy group looking into providing information and study into EMF stating that it’s services were no longer needed.
EMF is always going to be controversial, with one side clinging to their anecdotal evidence despite studies that prove otherwise. But it would appear that the verdict is in as far as the dangers of electrical and magnetic fields and that verdict is they are safe to be around.
Customcable.ca Launched to better serve Custom Cable Clients
After the success of cable5.ca and increase number of custom cable clients, MSASH Inc has launched its all new and improved website dedicated to custom cable assemblies.
The new website is to feature a number of direct RFQ order forms for D Sub Cables, Fiber optic cables, Networking Cables, Cisco Cables, coaxial cables and many more. The website will ultimately build a large knowledge base of Cable and Wire related topics, glossary terms and tools.
The new website also showcases some of the work MSASH Inc has performed for our customers over the years in the gallery section.